

Unlike traditional fuel vehicles, there is no significant technological gap between China is new energy vehicle industry and those of European and American automakers. Instead, with the support of policies, the industry has developed more rapidly. As early as 2015, China topped the global vehicle sales rankings with an absolute advantage of 330,000 units sold annually. With the introduction of the "dual carbon" goals, low-carbon emission reduction in the transportation sector has become increasingly urgent, further driving the development of the domestic new energy vehicle industry, which may help China achieve a breakthrough in the automotive sector.
Sales of new energy vehicles continue to hit new highs, with lithium battery safety issues receiving greater attention.
China is the fastest-growing new energy vehicle market globally. According to the September vehicle production and sales data released by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, the production and sales of new energy vehicles reached another historic high, with penetration rates further increasing. In September, production and sales of new energy vehicles reached 755,000 and 708,000 units respectively, representing year-on-year increases of 110% and 93.9%, with a market share of 27.1%. From January to September, cumulative production and sales reached 4.717 million and 4.567 million units respectively, representing year-on-year increases of 120% and 110%, with a market share of 23.5%.
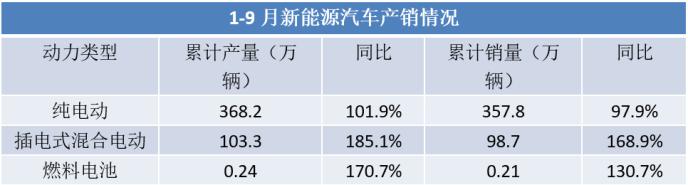
(Data source: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers)
New energy vehicles represent the future development direction of the automotive industry, with highly certain growth prospects. However, as new energy vehicles become more widespread, the safety of power batteries has increasingly become a major concern for the entire society. Accidents caused by spontaneous combustion and explosions of power batteries in new energy vehicles are frequent. According to data from the Fire and Rescue Bureau of the National Emergency Management Department, in the first quarter of 2022, there were 640 reported fire incidents involving new energy vehicles in China, marking a 32% year-on-year increase—higher than the 8.8% year-on-year growth in transportation-related fire incidents. On average, about seven fire incidents involving new energy vehicles occurred every day.
Power batteries are the "heart" of new energy vehicles, with the battery cell—composed of the cathode, anode, separator, and electrolyte—being the most critical component. The cathode materials mainly include ternary materials, lithium iron phosphate, lithium manganese oxide, and lithium cobalt oxide. Lithium batteries are categorized based on their cathode materials, with ternary lithium and lithium iron phosphate batteries dominating the current new energy vehicle power battery market. Both types of batteries have their own advantages and disadvantages. Ternary lithium batteries have higher energy density, providing longer driving ranges, but they come with higher costs, relatively poor stability, and shorter battery cycle life. Lithium iron phosphate batteries have lower energy density, resulting in relatively shorter driving ranges, but they are more cost-effective and offer better safety and stability. Tesla is new energy vehicles primarily use ternary lithium batteries, while BYD mainly equips its vehicles with lithium iron phosphate batteries.
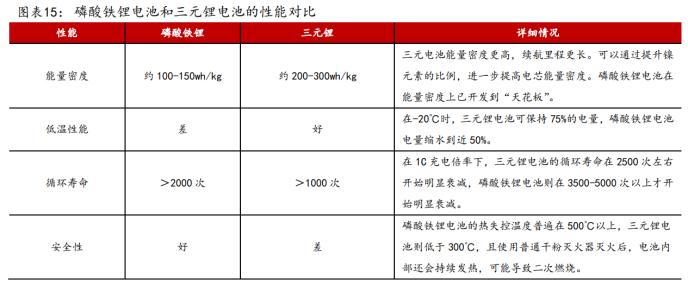
(Data source: Founder Securities)
Due to the relatively poor stability of ternary materials, their heat resistance is lower than 300°C, making them more prone to "thermal runaway," which is also one of the main causes of spontaneous combustion or even explosions in new energy vehicles. When thermal runaway occurs in a battery, decomposition and chemical reactions—such as reactions between electrodes and electrolytes, and melting of the battery separator—happen rapidly. These phenomena release a large amount of gas and heat. Once thermal runaway occurs in a single battery cell, it can quickly spread to other cells in the battery pack, causing a chain reaction. Therefore, once thermal runaway is triggered, accidents involving new energy vehicles are often unavoidable. When a battery pack malfunctions, enhancing its fire safety performance becomes critical to ensuring the overall safety of new energy vehicles.
The power battery pack of a new energy vehicle consists of multiple battery modules, with each module containing anywhere from a few to over a dozen battery cells. To achieve thermal protection for the battery pack, insulated and flame-retardant components are placed between each battery cell and each module. When a battery experiences "thermal runaway," these insulated and flame-retardant components can isolate the heat source, preventing high temperatures from spreading within the module. Thus, the performance of insulated and flame-retardant components is crucial to the safety of new energy vehicle battery packs.

Mica Flame-Retardant Components Effectively Enhance Power Battery Safety, with Broad Market Development Prospects
Flame-retardant components made from plastic materials are currently the main direction of market development, including materials such as PP, PA, PU, PC, and ABS, as well as various modified or composite materials derived from their combinations. While plastic-based flame-retardant panels offer relatively good overall performance, their flame-retardant properties are often less than satisfactory. The development of flame-retardant materials for power batteries remains an ongoing area of exploration and advancement.
Among these materials, mica stands out as an excellent insulating and heat-resistant protective material. Mica is a rock mineral with outstanding properties such as insulation, high-temperature resistance, high-pressure resistance, and alkali resistance. It also exhibits stable physical and chemical properties, making it widely used as an insulating material in the electronics and electrical industries. Additionally, mica finds extensive applications in industries such as automotive, cosmetics, inks, plastics, coatings, rubber, papermaking, construction materials, and metallurgy, earning it the nickname "industrial monosodium glutamate."
From the perspective of application structure, the main uses of mica are in refractory materials, insulating materials, and pearlescent pigments, accounting for over 80% of the market share. Mica-based insulating flame-retardant components, used as safety protective materials in new energy vehicle batteries, significantly improve electrical insulation and flame-retardant properties, greatly enhancing the safety of new energy power batteries and offering broad market potential.
Mica insulated flame-retardant components can be used for protection between battery cells. They not only isolate heat sources but also resist flame impact, effectively addressing the weakness of traditional aerogels in terms of impact resistance. Additionally, they accommodate the spatial requirements caused by expansion of battery cells with different chemical systems. These components can also serve as protective covers for entire modules, preventing flame impact and extending heat conduction time. The design includes directional explosion venting outlets to expel high-temperature gas flames, avoiding internal thermal spread within the module.
Domestic manufacturers have also made substantial progress in the research and development of mica flame-retardant components. It is reported that Universal Crystal, the world is largest synthetic mica producer (stock code: 06616.HK), has recently begun supplying synthetic mica-based insulated flame-retardant components for new energy batteries. The high-temperature resistance of their products has been tested up to 1,150℃, and their high-voltage breakdown resistance reaches 20KV/mm, significantly outperforming the plastic-based flame-retardant panels commonly used in the current market.

The company is insulated and flame-retardant component products feature excellent insulation properties, with a voltage breakdown resistance as high as 20KV/mm. They also demonstrate outstanding high-temperature resistance and flame-retardant performance, achieving a flame-retardant rating of UL94V-0. When exposed to flames at temperatures not lower than 1000°C, the flames do not penetrate. After combustion, the board surface only experiences slight discoloration, with the shape and strength remaining almost unchanged. The products exhibit superior bending strength and processing performance, allowing them to be processed into various shapes without delamination. Additionally, they offer excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and oils.
In the future, with the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry, power battery insulated and flame-retardant components using mica as the base material will be of great importance for enhancing the safety performance of lithium batteries, thanks to their outstanding insulation, high-temperature resistance, and flame-retardant properties. Synthetic mica may become an excellent insulation and thermal insulation material for new energy batteries, with broad development prospects.